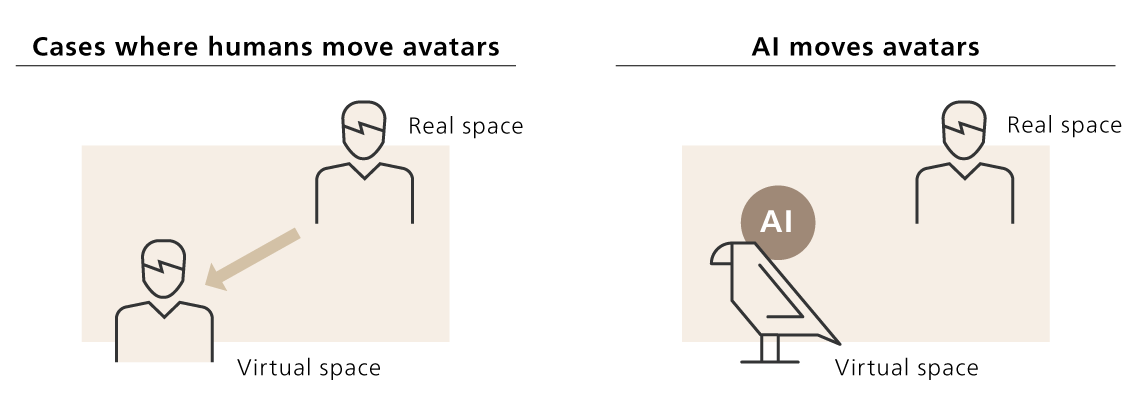
An e-soccer player B puts on a headset, heads to the virtual practice field in the metaverse space, and prepares for today's game.
Player B- "No virtual bird"
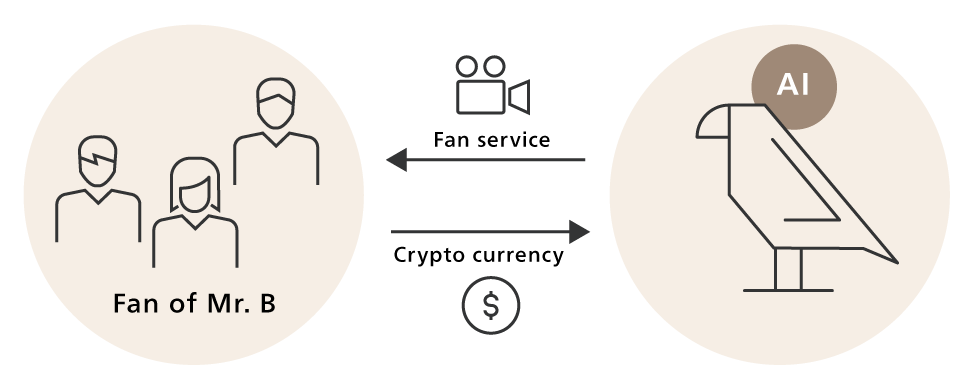
Player B is a famous e-soccer player. He always keeps the virtual bird on his shoulder, which is one reason for his popularity.
Player B - "The bird is supposed to return to the birdcage at a certain time, but where did it go? I have to go to the game soon. What's going on?"
The time was up. The player had no choice but to head to the virtual stadium. His teammate C was getting ready at the stadium ahead of him.
Teammate C - "Mr. B, thank you for your help today. No virtual bird today?"
Player B - "No bird. I went to the practice field today, but it was gone."
Teammate C - "Is that so? That's tough. Many supporters are looking forward to seeing that virtual bird.
Player B - "Yes, it is. Very troubled."
Then, waving his hand a little further away, service representative D from the insurance company came over.
Service Rep D - "Mr. B!"
Player B - "Hello, Mr. D. Thank you for the other day. What's up?"
Mr. D, a service rep, lifted the birdcage he was holding. Inside was Mr. B's virtual bird.
Service Rep D - "I found your virtual bird."
Player B - "Wow, thank you very much. I wonder how you did it? It's gone, and I was deep in distress."
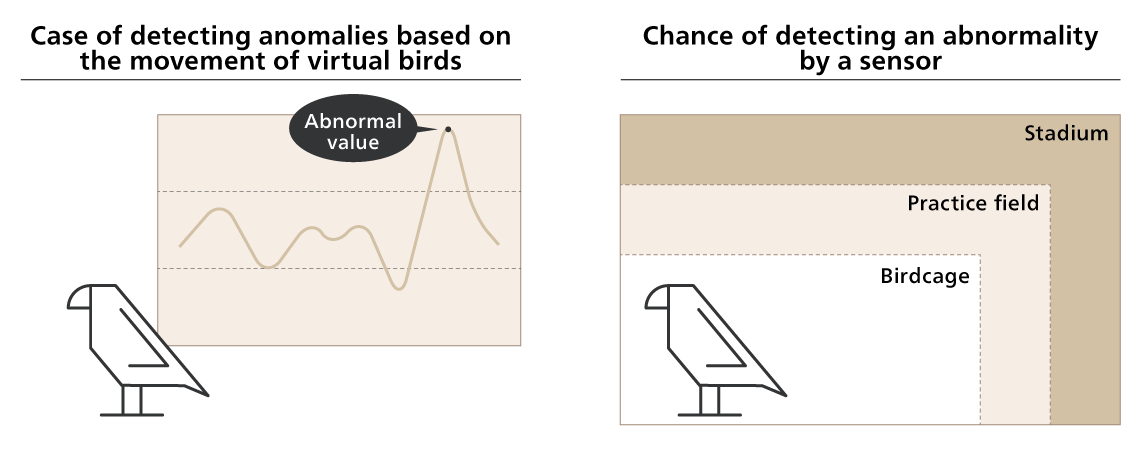
Service Rep D - "Last night, our insured management system detected an anomaly with Mr. B's virtual bird. Tracking it down, we found that while taking one photo after another with Mr. B's fans, the virtual bird got exposed to data that caused a malfunction and contracted an electronic disease. Therefore it failed to return to the birdcage. So, based on Mr. B's insurance policy for his virtual bird, we spotted the location of the virtual bird, treated it for the electronic disease, and then took it into custody."
Player B - "I got. That was very helpful. Thank you."
Service Rep D - "You insured this virtual bird just last month. We are glad you had it insured."