The external environment surrounding the procurement area is changing dramatically, with frequent occurrences of events causing global supply chain disruption and breakdown and legislation of environmental and human rights issues, particularly in Europe. Amid these changes, addressing increasingly complex and diverse supply chain risks is a key management agenda item. This article explains the challenges that need to be addressed in formulating and implementing long-term strategies for resilient and sustainable procurement, which will be essential for maintaining competitiveness in the future.
(This article was reconstructed based on the lecture "Resilient and Sustainable Procurement Strategy" from the webinar "Realizing Resilient and Sustainable Procurement Strategies and Improving Procurement Productivity Using AI" co-hosted by Qualtrics and ABeam Consulting on December 15, 2023.)
Realizing resilient and sustainable procurement strategies and improving procurement area productivity using AI
- SX
- Management Strategy/Reformation
Environment surrounding the procurement area and direction of response
In recent years, events causing global supply chain disruption and breakdown have become frequent, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, US-China trade tensions, and Russia's invasion of Ukraine. Concerns have also emerged regarding supply chain risks due to restrictions on rare minerals by certain countries like China. Meanwhile, the development of environmental legislation is advancing, triggered by the Paris Agreement's "1.5-degree temperature rise target," with movements particularly in Europe to require suppliers to set science-based targets (SBTs). Such changes in the procurement environment can lead to reduced competitiveness for the manufacturing industry.
It is clear that the challenges faced by procurement departments amid these external changes from a PEST (political, economic, social, technological) perspective cannot be resolved, in terms of politics, by companies alone in an increasing number of areas due to various regulations and legal frameworks such as carbon neutrality declarations, human rights due diligence, and the digital product passport (DPP). Procurement departments need to strengthen relationships with other suppliers and utilize collected information for ESG management and external communication.
Next, in terms of economy, procurement departments must detect supply chain risks such as semiconductor shortages and soaring oil/energy prices, and achieve reliable material procurement, cost reduction, and stable resource procurement. With regard to social aspects, challenges include declining birthrates, the aging population, the decreasing workforce, and workforce mobility. Actions such as operational productivity improvement, organizational transformation, and ESG management promotion are necessary while developing procurement talent. On the technological front, incorporating the latest technologies such as AI is a key and, in an era of information overload, major challenges include the digital implementation of procurement processes, AI utilization, and the development of procurement-related data infrastructure.
Bearing these factors in mind, at the root of procurement department challenges clearly lies an information strategy element of "catching and controlling accurate information in real time." The amount of information that needs to be managed and controlled for information strategy is huge, but the information can be broadly organized into “BSQCD,” which adds the perspectives of BCP (B) and sustainability (S) to the traditional QCD.
BCP consists of elements such as supply chain information related to suppliers, material risks, and logistics routes; risk information related to hazards and logistics disruptions; disaster information; infrastructure and organizational development; and economic security. For sustainability, environmental, social, and governance information needs to be captured in a timely manner. QCD demands continuous collection of accurate corporate information related to business partners (Figure 1).
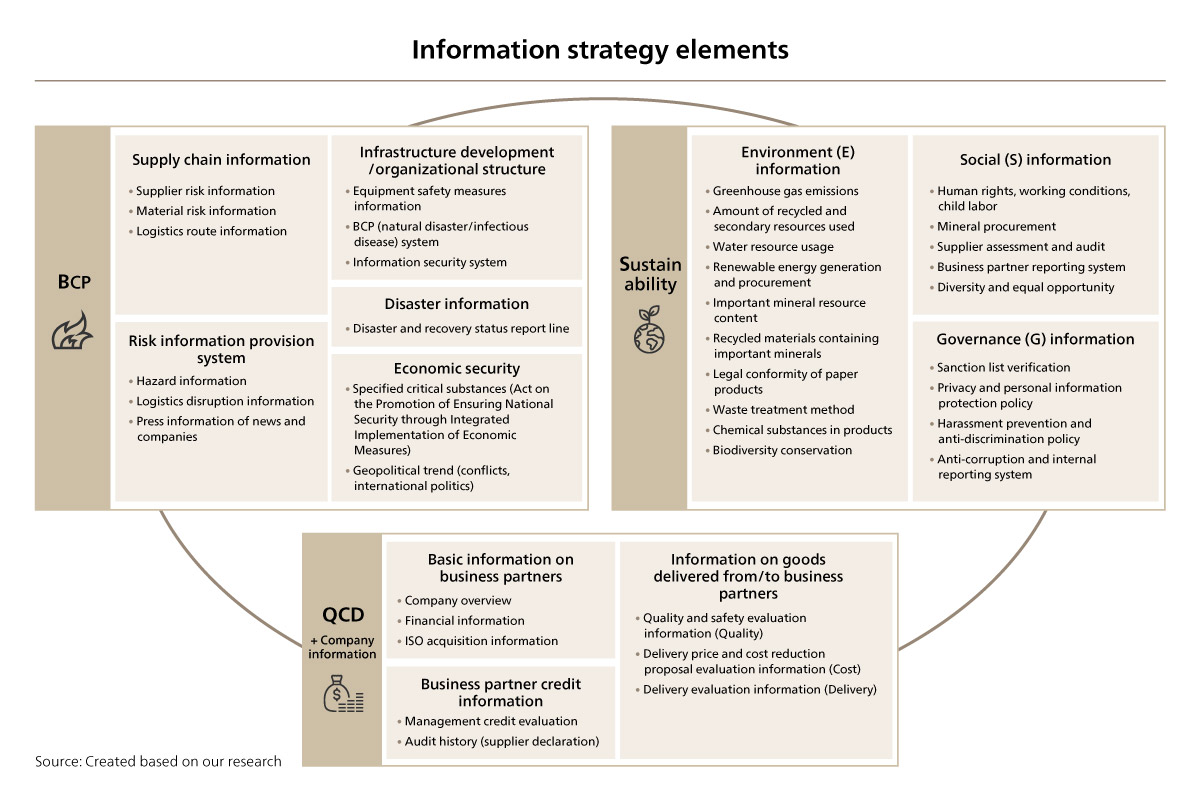 Figure 1 Information strategy of procurement department from BSQCD perspective
Figure 1 Information strategy of procurement department from BSQCD perspective
Need for long-term BSQCD strategy and its planning and execution scenario
Procurement departments must address various themes, as organized by the PEST analysis above. The core areas of "BSQCD long-term strategy" and "productivity improvement in the procurement area using AI" are particularly important.
However, the information elements of BSQCD are vast and cannot be comprehensively grasped and addressed overnight. For instance, to formulate and execute a "BSQCD long-term strategy" while solidifying the foundation based on BSQCD information defined by a long-term vision toward 2030, "productivity improvement in the procurement area using AI" is essential. Process transformation maximizing AI utilization and digital empowerment aligned with business objectives, both discussed below, can improve productivity, freeing up capacity. Determining priority initiatives and redirecting the capacity created through AI utilization leads to the advancement of operations and ultimately enables the realization of a BSQCD long-term strategy (Figure 2).
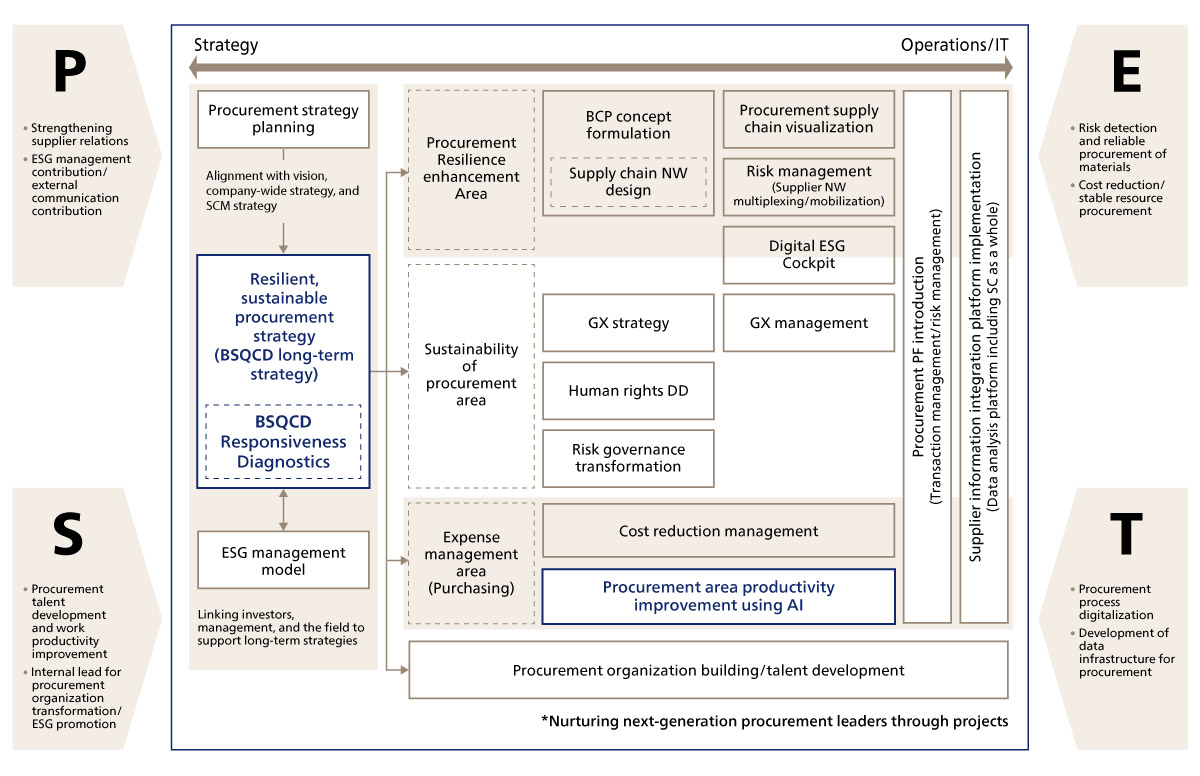 Figure 2 Procurement department challenges identified through PEST analysis
Figure 2 Procurement department challenges identified through PEST analysis
A BSQCD long-term strategy requires development by backcasting from the future to the present after defining key issues and clarifying the ideal state. As a roadmap example, with "strengthening stakeholder responsiveness" established as a company-wide vision for 2030, milestones could be set such as "enhancing supplier information acquisition" and "information visualization" by 2024, and "supplier evaluation/selection" and "collaborative improvement activities" by 2026, establishing a path to the goal.
Implementing a BSQCD long-term strategy also requires the development of an information integration platform for utilizing various data. First, data is collected and analyzed in respective BCP, sustainability, and QCD systems, and then integrated and centralized as a supplier information integration platform for use by various internal departments. Next is the crucial step of linking and integrating the data of each system while making the most of existing assets, and allowing each department to view necessary data at the required granularity. ABeam Consulting provides support for the introduction of tools that enhance and streamline information collection, analysis, storage and integration, and has a track record of introducing many such tools, including Qualtrics' “XM for Suppliers” (Figure 3).
In practicing ESG management, importance also lies in quantitatively demonstrating how activities are linked to increases in corporate value in accordance with the ESG management model. For example, our ESG Data Analytics uses the "Yanagi Model" theory (proposed by our advisor Ryohei Yanagi for quantifying ESG management) to visualize how much the duration of activities can impact corporate value. Some analysis results show that "increasing the percentage of female managers by 1% leads to a 5.6% improvement in PBR (Price-to-Book Ratio) after 5 years" and "reducing greenhouse gas emissions by 10% leads to a 3.4% improvement in PBR after 8 years."
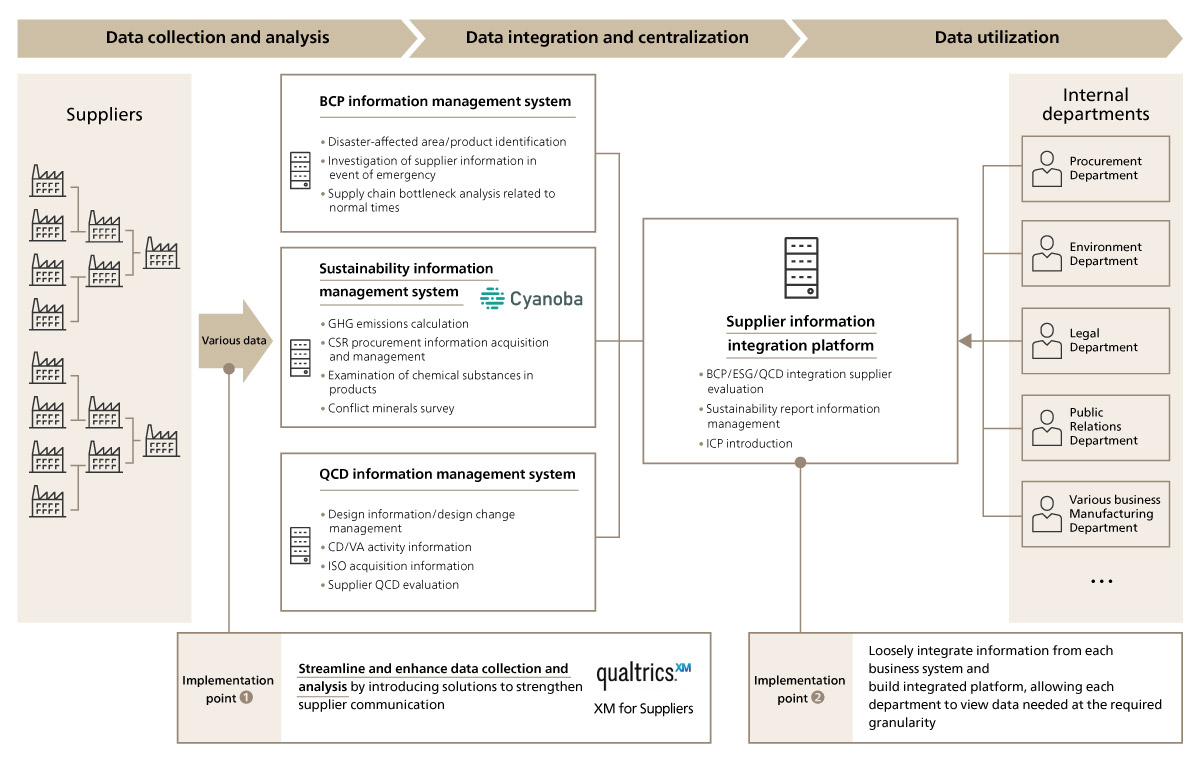 Figure 3 Architecture of information infrastructure essential for implementing BSQCD long-term strategy
Figure 3 Architecture of information infrastructure essential for implementing BSQCD long-term strategy
Freeing up capacity by improving productivity in the procurement area using AI
In traditional procurement, a vicious cycle exists where inefficient business processes create staff shortages, which in turn prevents efficiency improvements. This is caused by multiple interconnected factors: reliance on manual labor and experienced employee expertise, outdated systems, perfunctory BCP responses, overwork due to chronic understaffing, lack of execution capability for advanced strategies, and low morale due to loss of talented personnel.
The key to solving these issues is digital empowerment through AI utilization. While tool implementation alone is not sufficient and must be coupled with elements such as business-aligned transformation concepts, organizational transformation, and HR measures, the capacity freed up by AI utilization undoubtedly drives other transformations.
For example, how can AI improve the efficiency of quote creation tasks, a common challenge for many companies?
First, interactions between the departments and the suppliers involved in quote requests can be replaced by generative AI like ChatGPT. AI-based recommendation functions can also be applied to sourcing tasks that typically rely on the knowledge of experienced personnel. Using AI meeting minutes and the like for supplier negotiations allows human resources to focus on advanced tasks such as logic creation.
The key to implementing AI and digital solutions is to take a panoramic view of the entire process, rather than just the tools, and to apply the appropriate digital technology after identifying the areas having the greatest workload and challenges. AI utilization and outsourcing in areas with high workload typically yield significant effects and easily free up capacity. Such transformation should basically progress in phases - basic concept, design, and implementation - after establishing the project structure. Note that conducting a transformation opportunity assessment at the very beginning can provide a cost-benefit outlook and facilitate actualization.
Then, before redirecting the extra capacity created through the use of AI to the BSQCD strategy, clarifying the current situation is important. This enables analysis and visualization of gaps between the ideal state and current state, and clearly defines organizational challenges, facilitating the development of appropriate measures while prioritizing them.
We have prepared “BSQCD Responsiveness Diagnostics” that organically captures and promotes the process of visualizing the current situation, identifying the gaps (issues) between the current state and the ideal state, and examining measures to achieve the ideal state.
For example, we applied our diagnostics to an electrical equipment manufacturer and identified large gaps between the current state and the ideal state in material-specific responsiveness. The diagnostics found significant perception gaps between management and field staff in terms of GHG emission targets, and revealed differences in understanding among staff about implemented systems. "BSQCD Responsiveness Diagnostics" proved to be a useful tool in exposing issues such as ongoing initiatives not permeating throughout the organization (Figure 4).
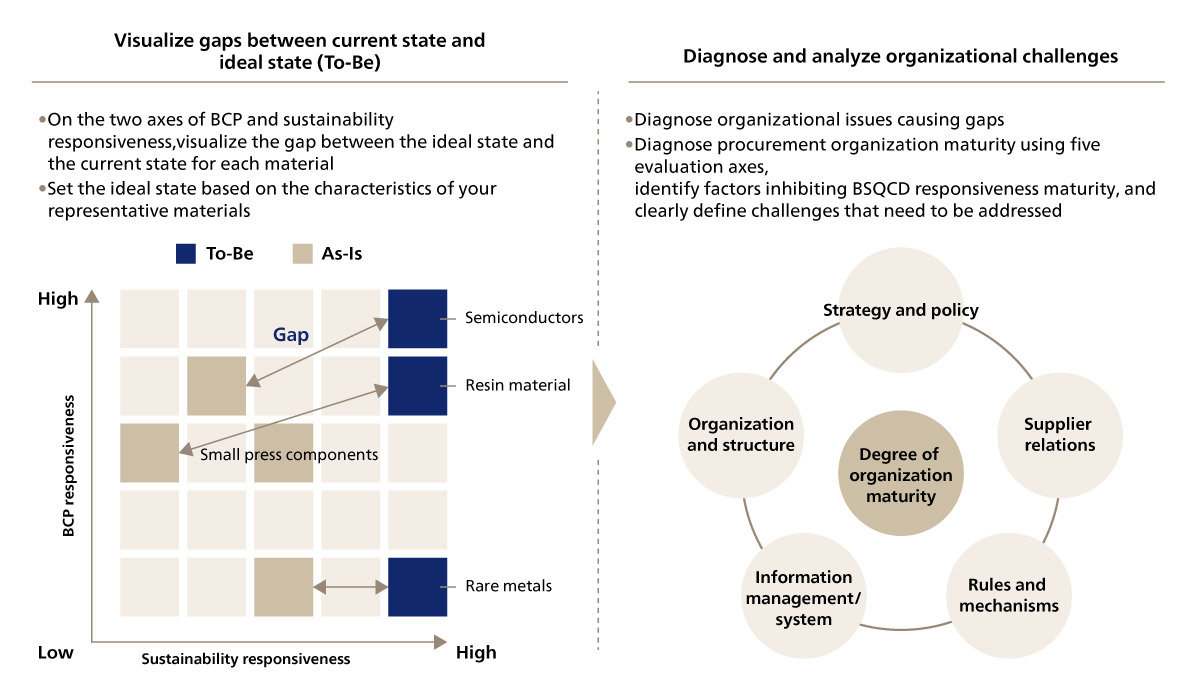 Figure 4 Overview of BSQCD Responsiveness Diagnostics
Figure 4 Overview of BSQCD Responsiveness Diagnostics
Lastly, procurement strategies incorporating BCP and sustainability perspectives are becoming increasingly important, and companies lagging in these areas will likely see reduced competitiveness. We hope to see companies envision a long-term scenario for achieving BSQCD, clarify priorities through diagnostics while freeing up capacity by using the latest technologies like AI, and efficiently work toward the ideal state.
ABeam Consulting is providing ongoing support for long-term BSQCD strategies, leveraging our extensive experience in both developing and implementing DX strategies. With a track record of achieving many results in projects for Japanese manufacturing industries, we propose grounded solutions tailored to individual situations, such as AI productivity improvement and BSQCD diagnosis. Furthermore, utilizing our strength in establishing Japan's first ESG management model that has gained market credibility, we guide the implementation of long-term strategies while aligning onsite BSQCD activities with management’s commitment to its investors.
Click here for inquiries and consultations
