Vietnam’s pharmaceutical market is undergoing rapid transformation, driven by rising healthcare demands, an aging population, and improving business environment. With an anticipated annual growth rate of 5%, the market is expected to reach US$2.43 billion by 2025 [Figure. 1]. Consumers, with increasing disposable income and aging population, are seeking high-quality, innovative, and specialty pharmaceuticals, creating opportunities for both domestic and international pharmaceutical companies. This growth has been supported and is in parallel with Vietnam's favorable supply of workers and improvements in logistics infrastructures. This paper explores the key drivers of Vietnam’s pharmaceutical market expansion, the evolving regulatory landscape, and the opportunities available for pharmaceutical companies looking to establish or expand their presence in the country.
#3 ABeam Consulting shares insight on Vietnam’s pharmaceutical sectors’ opportunities, challenges, and entry approaches for New Entrants
- Health Care
- Machinery
- Supply Chain Management
- Data-Driven Management

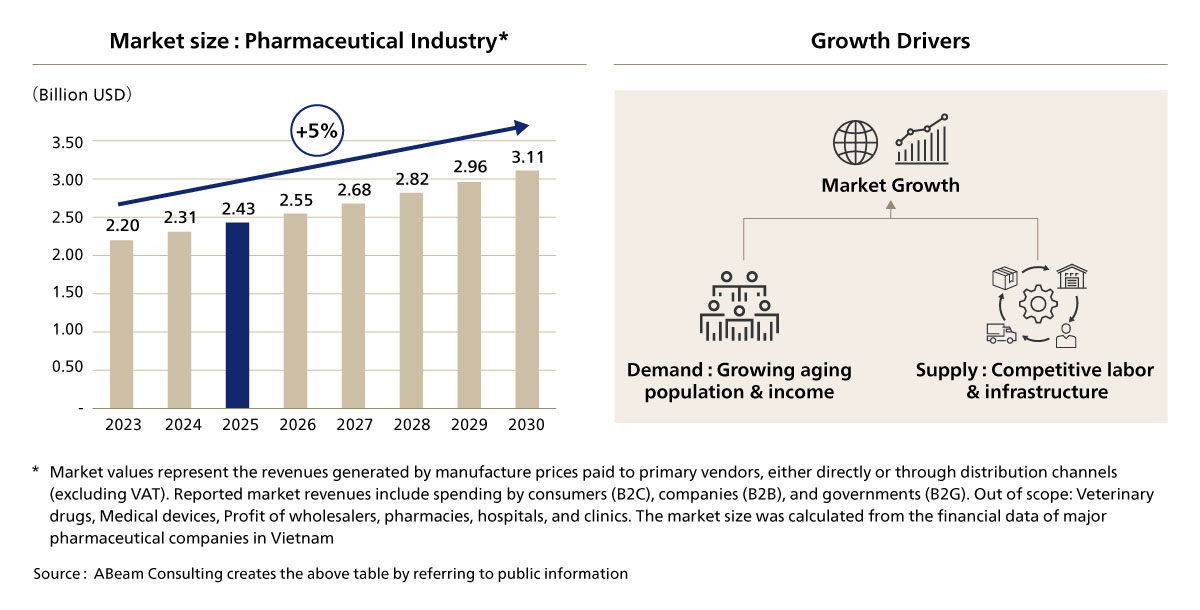 Figure 1. Vietnam Pharmaceutical Market Size & Drivers
Figure 1. Vietnam Pharmaceutical Market Size & Drivers
-

Tetsuya Ueda
Manager -

Dan Samitisirisuk
Senior Consultant -

Chanon Prapasphen
Consultant
The increase in the population aged 65 and above in Vietnam, combined with rising GDP (Gross domestic product) per capita, is significantly driving the demand for pharmaceuticals in the country [Figure. 2]. As the aging population grows, particularly in a society with a rising life expectancy, there is a corresponding increase in the need for healthcare services, chronic disease management, and age-related treatments. This demographic shift contributes to a higher consumption of pharmaceutical products, especially those for managing conditions such as cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and cancer. At the same time, Vietnam's rising GDP per capita reflects an improvement in the standard of living and disposable income, allowing a larger portion of the population to afford better healthcare services, including prescription medications. As both the elderly population and income levels increase, the demand for pharmaceutical products in Vietnam is expected to continue to grow, presenting opportunities for both local and international pharmaceutical companies.
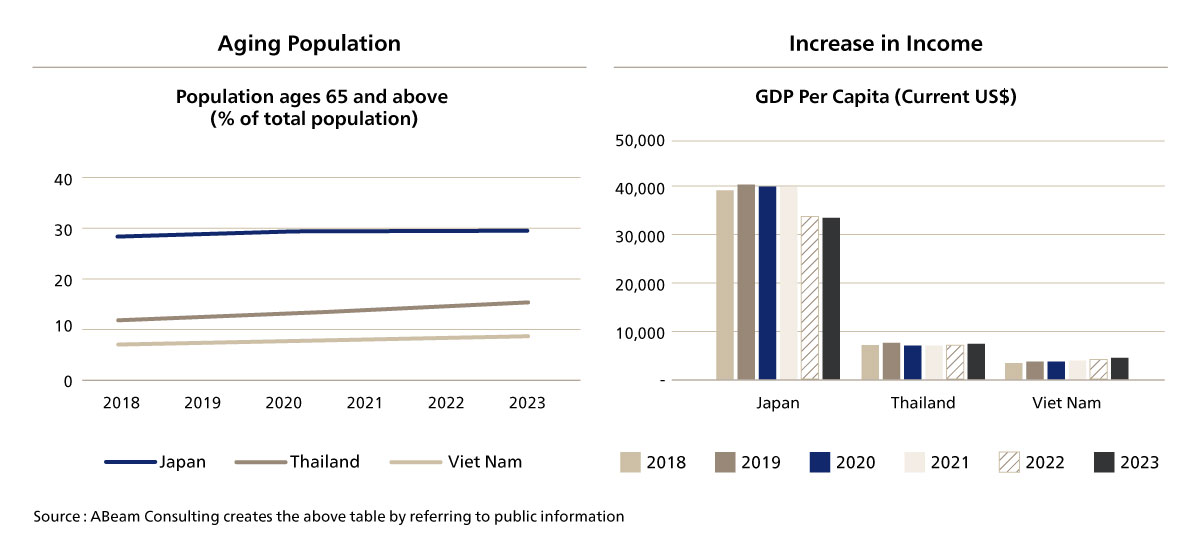 Figure 2. Demand-Side Drivers
Figure 2. Demand-Side Drivers
Additionally, Vietnam's pharmaceutical industry is growing rapidly due to several key supply-side drivers [Figure. 3]. The country benefits from a developing pool of skilled workers in pharmaceutical manufacturing, research and development, and regulatory compliance, which enhances the industry’s ability to meet global standards. Vietnam’s competitive labor costs and cost-effective manufacturing processes make it an appealing location for pharmaceutical production, allowing companies to reduce production costs and provide affordable medicines. Additionally, significant investments in infrastructure, such as improvements in transportation, communication, and healthcare facilities, support the efficient production and distribution of pharmaceutical products. These combined factors create a robust foundation for the continued growth and expansion of the pharmaceutical industry in Vietnam.
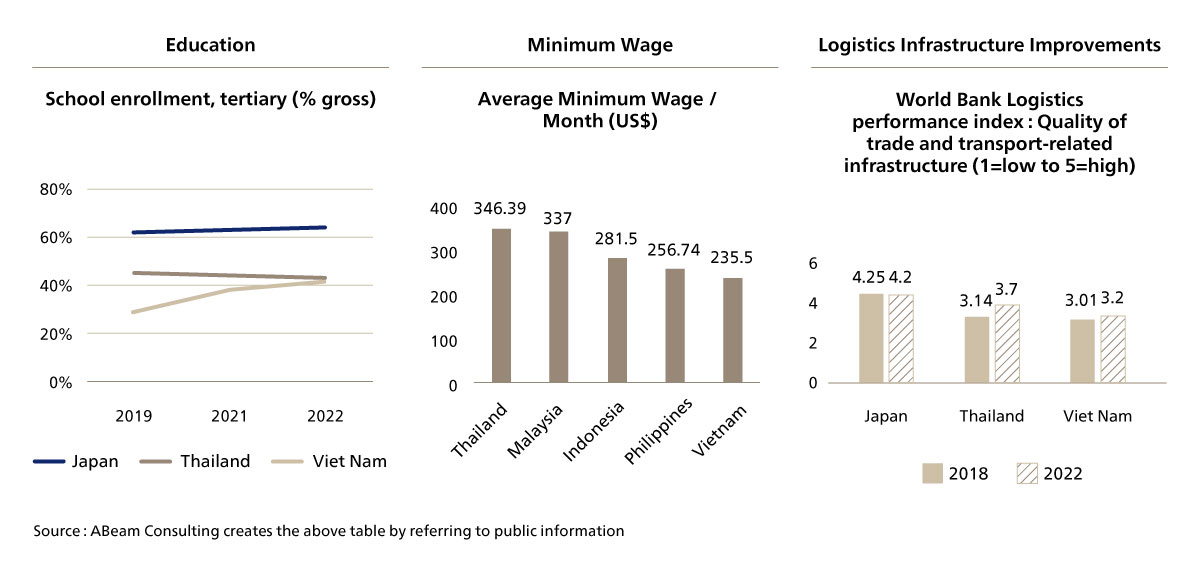 Figure 3. Supply-Side Drivers
Figure 3. Supply-Side Drivers
However, Foreign pharmaceutical companies still face significant regulatory restrictions in Vietnam, as the government does not permit them to directly engage in the importation or distribution of pharmaceutical products. This creates a considerable challenge for foreign firms seeking market entry, as they must navigate complex licensing processes and rely on local distributors or establish partnerships with domestic entities to operate within the country. However, a notable advantage is that Vietnam does not strictly regulate pharmaceutical selling prices, allowing foreign companies greater pricing flexibility compared to markets with stringent price controls. This regulatory environment presents both obstacles and opportunities, requiring strategic approaches for foreign pharmaceutical firms to successfully enter and compete in Vietnam’s growing healthcare market.
Strict regulations by the government that prohibits foreign companies from directly engaging in importation and distribution of pharmaceuticals, necessitating partnerships with local entities. As depicted in the value chain [Figure. 3], foreign firms such as Sanofi and Hisamitsu can obtain import and manufacturing licenses but must outsource wholesale distribution to local partners or subsidiaries. Companies like DKSH and Zuellig Pharma specialize in import services but do not participate in direct retail distribution. Meanwhile, domestic companies such as Gigamed, Hoang Duc, and Imexpharm hold full-spectrum licenses, enabling them to manufacture, import, and distribute pharmaceuticals within the country. The retail sector is dominated by local pharmacy chains, reinforcing the necessity for foreign companies to navigate Vietnam's regulatory framework strategically.
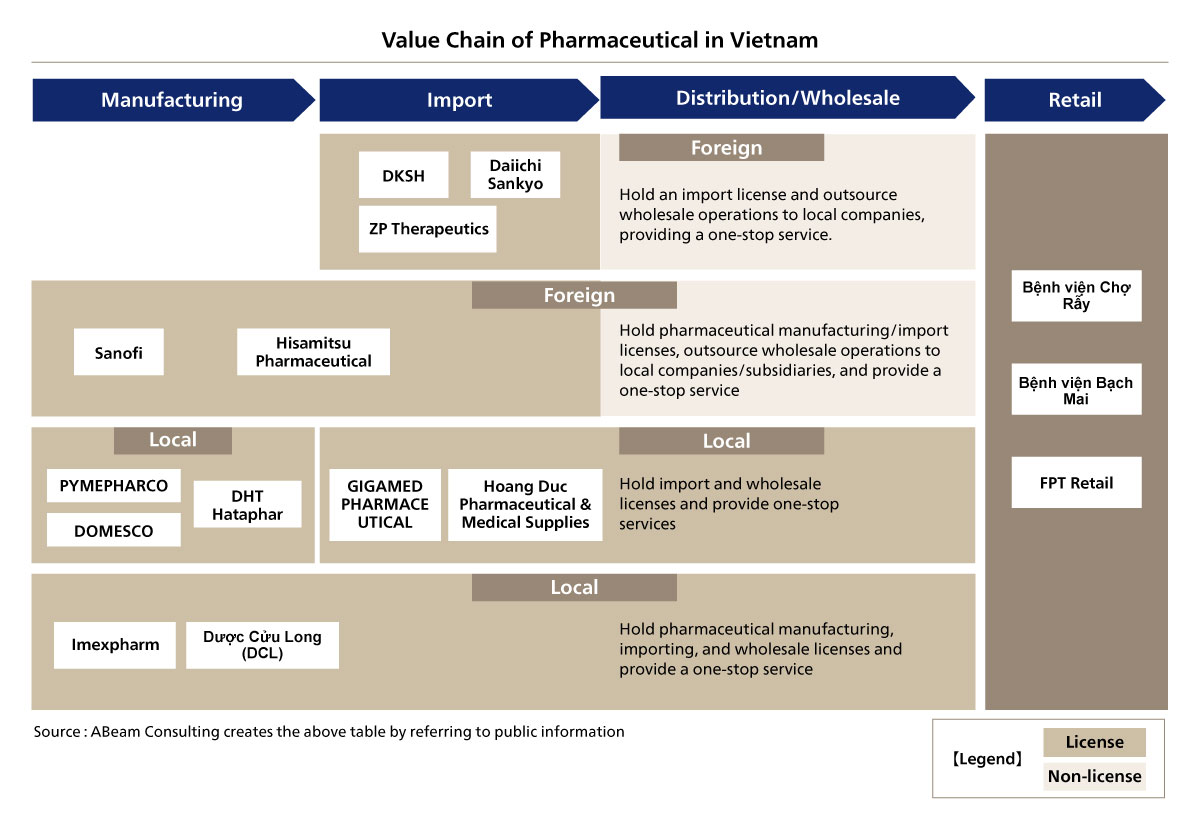 Figure 4. Vietnam Pharmaceutical Value Chain
Figure 4. Vietnam Pharmaceutical Value Chain
Considering these constraints, companies looking to enter Vietnam’s pharmaceutical market must navigate strict regulatory barriers that prohibit foreign firms from directly importing or distributing pharmaceutical products. As a result, market entry strategies typically involve partnerships with local entities. Establishing a wholly owned subsidiary (WOS) is possible but comes with regulatory challenges, requiring foreign companies to focus on manufacturing rather than distribution. Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) offer a viable route to gain local market access by acquiring existing pharmaceutical manufacturers or distributors. Joint ventures (JV) with Vietnamese firms help foreign companies share risks, resources, and market expertise. Outsourcing through Contract Sales Organizations (CSOs) allows foreign companies to leverage local distributors for marketing and distribution without direct involvement. Licensing and franchising models enable foreign pharmaceutical firms to authorize local companies to manufacture or distribute their products. Direct exporting remains an option but requires collaboration with licensed local importers. Given Vietnam’s evolving regulatory landscape, companies must strategically select their market entry approach to ensure compliance while maximizing market opportunities.
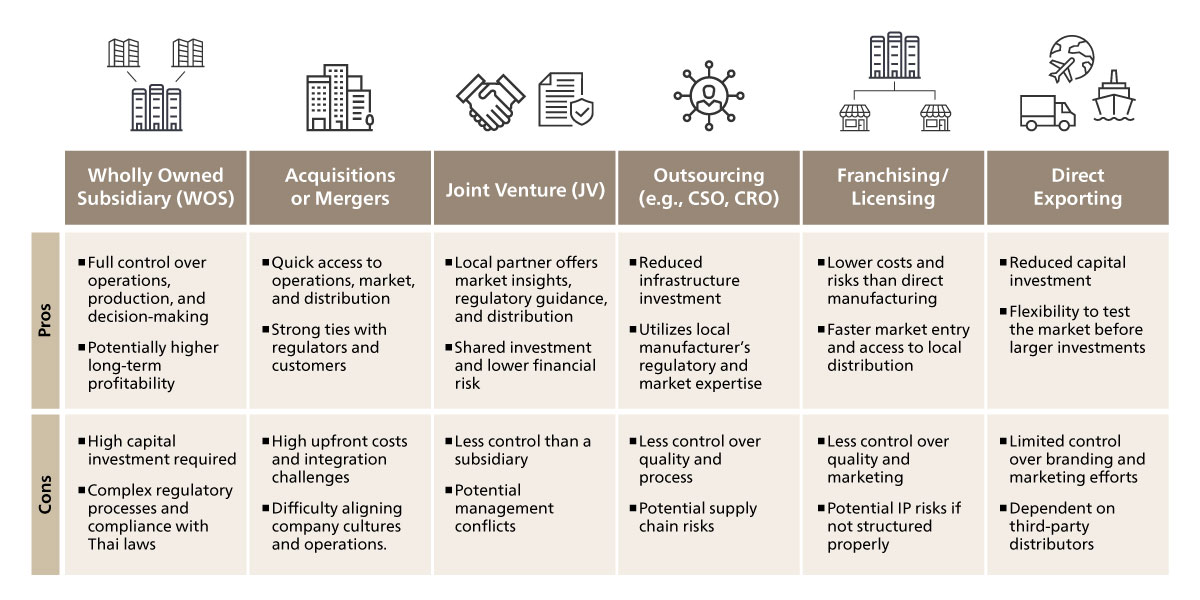 Figure 5. Common Market Entry Options
Figure 5. Common Market Entry Options
To conclude, Vietnam’s pharmaceutical market presents significant growth opportunities for new entrants despite its regulatory challenges. The government’s ongoing investment in healthcare infrastructure create an encouraging environment for market entry. Success in Vietnam’s pharmaceutical sector requires a strategic approach, leveraging partnerships with local distributors, utilizing Contract Sales Organizations (CSOs) for market access, and capitalizing on the rising demand for high-quality, innovative medicines. By aligning with Vietnam’s evolving healthcare trends and regulatory landscape, businesses can establish a strong and sustainable presence in this rapidly expanding market.
Insights
- #1 ABeam Consulting shares insight on Thailand’s pharmaceutical sectors’ opportunities, challenges, and entry approaches for New Entrants
- #2 ABeam Consulting shares insight on Key Considerations for CSO Partnerships in the Thai Pharma Market: Marketing & Sales Focus
- #3 ABeam Consulting shares insight on Vietnam’s pharmaceutical sectors’ opportunities, challenges, and entry approaches for New Entrants
Click here for inquiries and consultations
