This Insight gives an overview of the business impact caused by the evolution of generative AI, the widespread adoption of large language models (LLMs), and the addition of new functionality. Our independent survey indicates that the use of AI in business operations has become easier and companies are aiming to improve their efficiency and generate new value with it. This article also covers predictions on the growth of the generative AI market and concerns regarding company policies on AI usage The upcoming six articles in this Insight series give specific usage methods and case studies, clarify the importance of AI governance, and offer detailed guidelines for the adoption of generative AI by companies.
Generative AI-Driven Business Revolution: Seven Keys to Success for Producing Outstanding Results. Part 1: Generative AI-Driven Business Revolution
- Technology Transformation
- Cloud
- AI

Ever-evolving LLMs
In September 2024, ChatGPT grew to become an app with over 200 million users in a single week, increasing the widespread embedding of generative AI in our everyday lives.
The popularizing of generative AI made explosive progress when ChatGPT arrived on the scene in 2022. Its accuracy and response speed improved with the subsequent release of GPT-3.5, and with this release, its use in business took a step further.
GPT-4o was released in May 2024, making it possible to not only generate text like before but also audio and images, as well as text based on audio and images. These advances made multimodal processing possible. Then, in September 2024, with the emergence of OpenAI’s o1, which has the ability to generate “long chains of thought” internally, it became possible to generate highly accurate answers for tasks requiring deep thinking such as mathematical problems or logical puzzles that it was previously poor at. In just over two years since the birth of ChatGPT, the accuracy of LLMs has improved significantly, with its scope of use and potential expanding dramatically.
A new phase of generative AI
In July 2024, some media outlets reported that OpenAI had created a five-level criteria system for evaluating the progress of LLM’s artificial general intelligence (AGI). More specifically, AGI is defined as starting from Level 1 with simple conversational abilities, possessing more advanced problem-solving capabilities at Level 2, and being an agent capable of autonomous action at Level 3. Later on, Level 4 would be defined as being an innovator that produces new ideas that contribute to the knowledge of humankind. Lastly, Level 5 would be defined as evolving into an AI capable of running an entire organization autonomously. While it is uncertain whether generative AI will evolve in this way and how long the process will take if indeed it does, it is an extremely useful set of definitions that can be used as a measure for examining how the scope of AI application grows and how it impacts business.
So, what level is generative AI at currently? Generative AI reached Level 2 with the emergence of OpenAI o1, and more recently, agent AIs corresponding to Level 3, such as GPT Researcher, are beginning to be integrated into various services. We have already entered the phase where AI agents can plan, make decisions, and act on their own to achieve the targets it has been given. A race to develop solutions has begun.
By generative AI utilization becoming multimodal and processing becoming agent-driven, it is possible to transform how data is managed. Integrated platforms have emerged that utilize “ontology” to manage data such as internal structured data, unstructured data, IoT data, and geospatial data by assigning meaning and relationships from a business perspective. A world in which end-to-end business processes can be executed by the generative AI on these integrated platforms is becoming increasingly realistic. It is fair to say that the automation of business processes and data management to achieve this are advancing into uncharted territory.
The use of AI in business operations is simpler than ever
Before the emergence of generative AI, in AI projects, it was common to use models that had already been trained. In the field of computer vision, models pre-trained on ImageNet were widely used. Meanwhile, in the field of natural language processing, pre-trained models such as Word2Vec and BERT were used for many tasks. Models were also adapted to specific tasks or domains through transfer learning. Data scientists were required to make this happen and there were also certain hurdles to using published models.
However, LLMs in recent years have become universal, high-performance models. We can now easily use these models for a wide range of tasks such as summarizing, translation, and searching. The fine tuning is no longer required and the prompt-based approach that can execute individual tasks just by submitting prompts has significantly changed how people think of AI model construction and AI usage. The lowering of the hurdle that stood in the way of making it possible to apply models to business operations without data scientists has made AI more user-friendly. Discussions now focus on how to effectively use these models in business operations to get the best output from what you put in and how to use generative AI to make business operations more efficient and generate value.
Generative AI market expansion and company policies on AI usage
The generative AI market is growing rapidly. According to the Japan Electronics and Information Technology Industries Association (JEITA), the generative AI market in Japan is expected to reach 118.8 billion yen in 2023, 687.9 billion yen in 2025, and 1 trillion and 777.4 billion yen in 2030. The growth rate is 47.2% on average annually, with generative AI foundation models, related applications, and solution services all increasing at great speed. In particular, the market for generative AI-related applications accounts for 80% of this growth. It is expected that generative AI will be incorporated into all kinds of applications in the coming years.
In terms of the initiatives of each company, according to 2024 White Paper on Information and Communications in Japan, the percentage of Japanese companies that have outlined a generative AI policy is 42.7% (the total of those with “Going to actively utilize” or “Going to utilize in limited areas”*1). In the same report, regarding the benefit and impact of using generative AI, about 75% of companies responded that it would “Lead to improvement of business efficiency and resolvement of personnel shortage” Meanwhile, 70% of companies indicated that would “Increase in possibilities to infringe rights such copy rights” Companies also have concerns over the “Increase in possibilities to infringe rights such as copy rights”. This has risen to as many as approximately 70% of companies, highlighting worries over the risks of generative AI.
*“2024 White Paper on Information and Communications in Japan” published by Japan’s Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications
https://www.soumu.go.jp/johotsusintokei/whitepaper/eng/WP2024/pdf/01-chap5_sec1.pdf
The benefits of using generative AI
Although there are challenges such as security risks, some companies have begun examining the use of generative AI or undertaking a PoC because it offers large potential benefits. More and more companies are also starting to use generative AI in their business operations. ABeam Consulting is also engaged in projects that utilize generative AI for all kinds of companies and organizations, regardless of the type of business or industry. Last fiscal year there were quite a lot of PoCs conducted for response and inquiry operations with Retrieved-Augmented Generation (RAG), which generates answers from internal information. This fiscal year has seen further considerations given to using generative AI in marketing and system development domains.
How do companies assess the benefits of using generative AI, which has started to be deployed at some companies? In a survey on the use of generative AI by business men and women conducted by ABeam Consulting, 47.2% of those involved in the deployment of generative AI responded that they were already using it at work (see Figure 1). Also, of the respondents who are already using generative AI, 78.8% said they experienced benefits exceeding their expectations. This gives us a sense that most companies that have started using generative AI are now able to utilize it effectively (see Figure 2).
In checking the benefits of deploying generative AI for different uses, approximately 83% of the “AI system development through internal development” respondents experienced benefits exceeding their expectations. This significantly surpasses the 69.5% of those “Using existing SaaS platforms” (see Figure 3).
As reasons why the benefits of using generative AI produced results exceeding expectations (phases in which it contributed to results), “Launching generative AI projects, formulating a vision, and/or identifying use cases” received 39.2%, “Organizing the requirements that generative AI systems or services must meet” received 36.6%, and “Building verification environments, implementing technical verifications, and conducting comparative evaluations of generative AI systems or services” received 11.6% (See Figure 4).
Meanwhile, as for reasons why the benefits of using generative AI did not meet expectations (phases in which efforts were insufficient and failed to meet expectations), “Organizing the requirements that generative AI systems or services must meet” received 33.8%, “Building verification environments, implementing technical verifications, and conducting comparative evaluations of generative AI systems or services” received 26.2%, and “Launching generative AI projects, formulating a vision, and/or identifying use cases” received 17.2% (See Figure 5).
Generative AI has various options for how it can be used, such as internal development or utilizing existing SaaS services. Many of the companies that are using it experience its benefits. “Formulating a vision and/or identifying use cases” and “Organizing the requirements that generative AI systems or services must meet” in the upstream phase are especially important for experiencing the benefits of generative AI in using it for business purposes. From the fact that utilizing generative AI was more likely to offer benefits in internal development than using existing SaaS services, we can see that utilizing generative AI was more likely to provide a positive impact when used in ways aligned with each company’s vision and specific requirements.
On the other hand, those who responded that the results of deploying generative AI did not meet expectations gave “Building verification environments, implementing technical verifications, and conducting comparative evaluations of generative AI systems or services” as the reason why. From this, we can infer that the reviewing of upstream requirements and use cases, including an evaluation of its technical feasibility, was insufficient. It is important to examine the use of generative AI, including from a technical perspective, from the stage of formulating a vision or examining use cases.
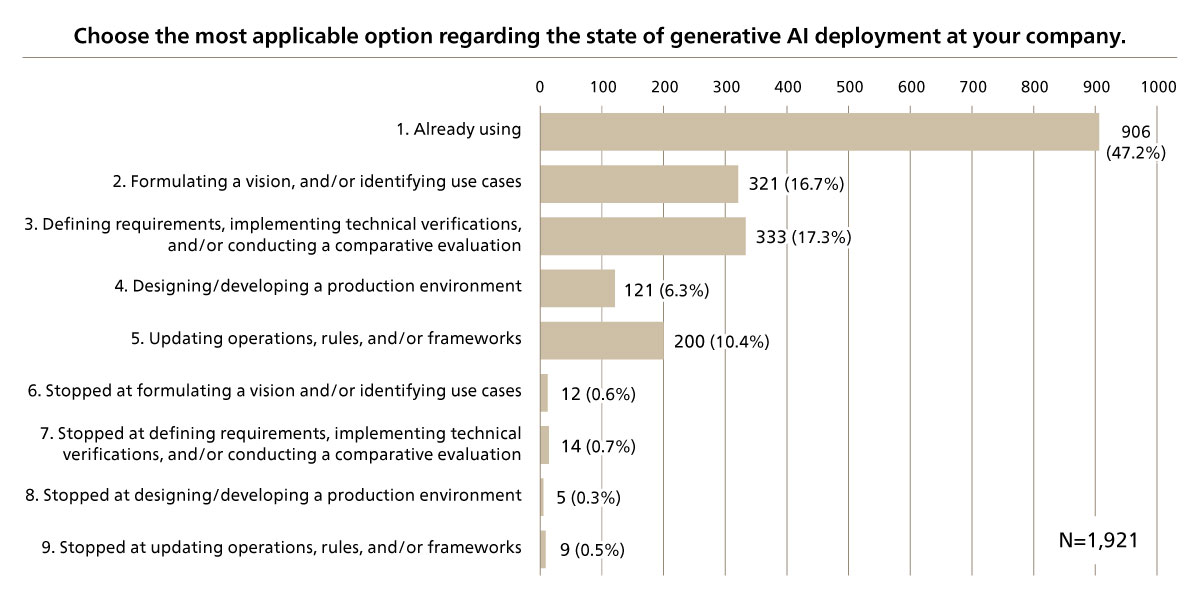 Figure 1 Status of Generative AI Implementation
Figure 1 Status of Generative AI Implementation
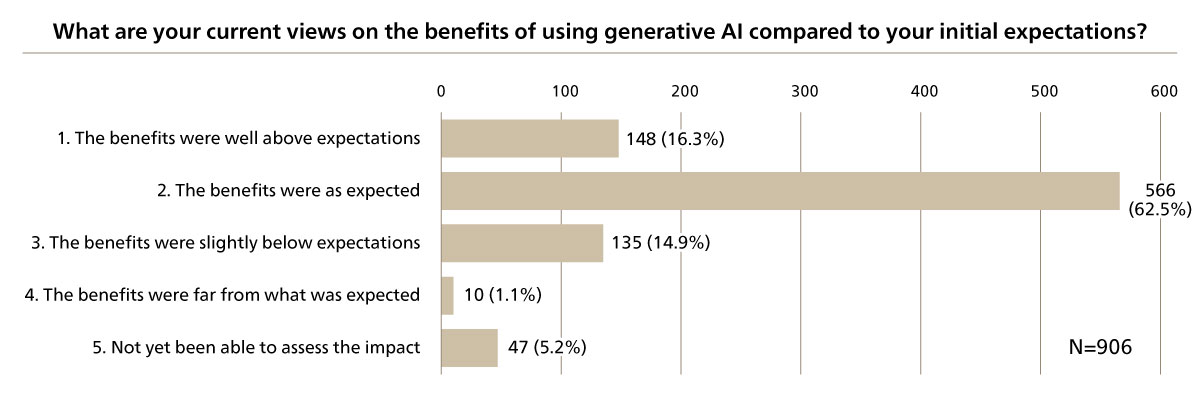 Figure 2 Effectiveness of Generative AI Utilization
Figure 2 Effectiveness of Generative AI Utilization
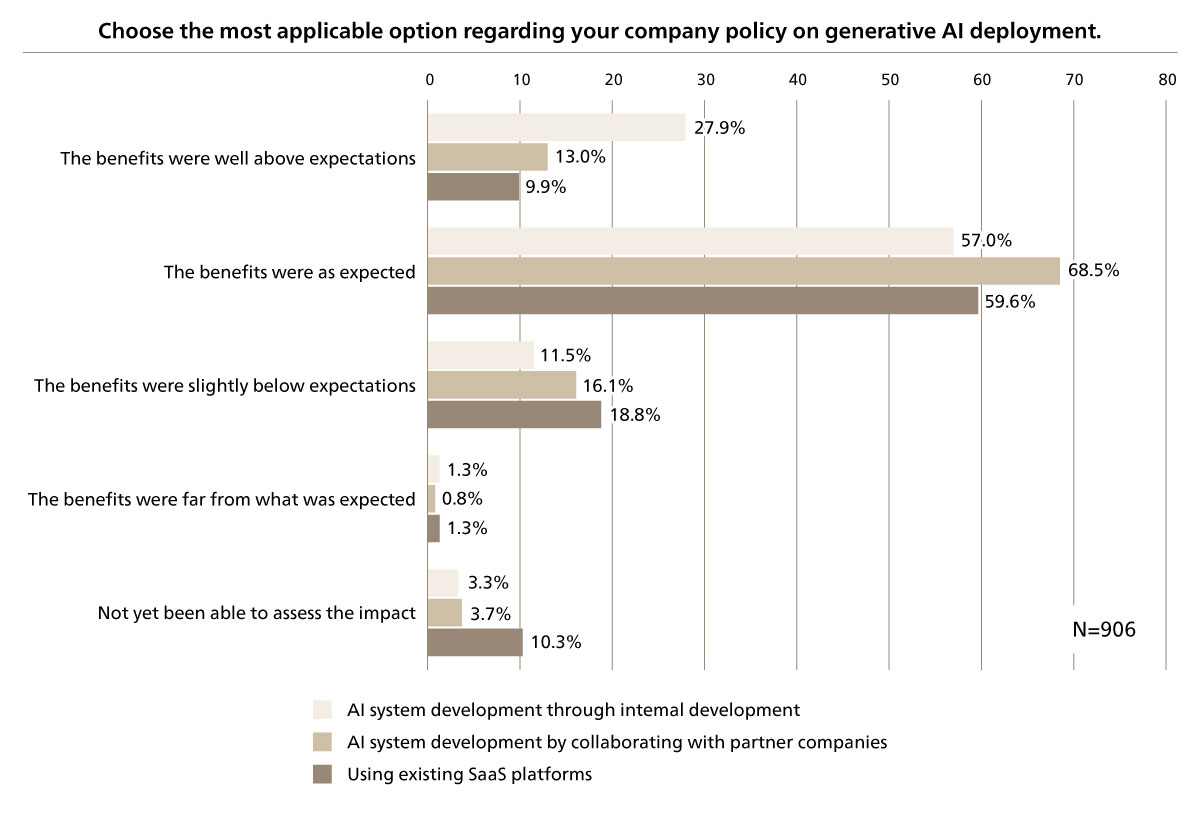 Figure 3 Policy for Implementing Generative AI
Figure 3 Policy for Implementing Generative AI
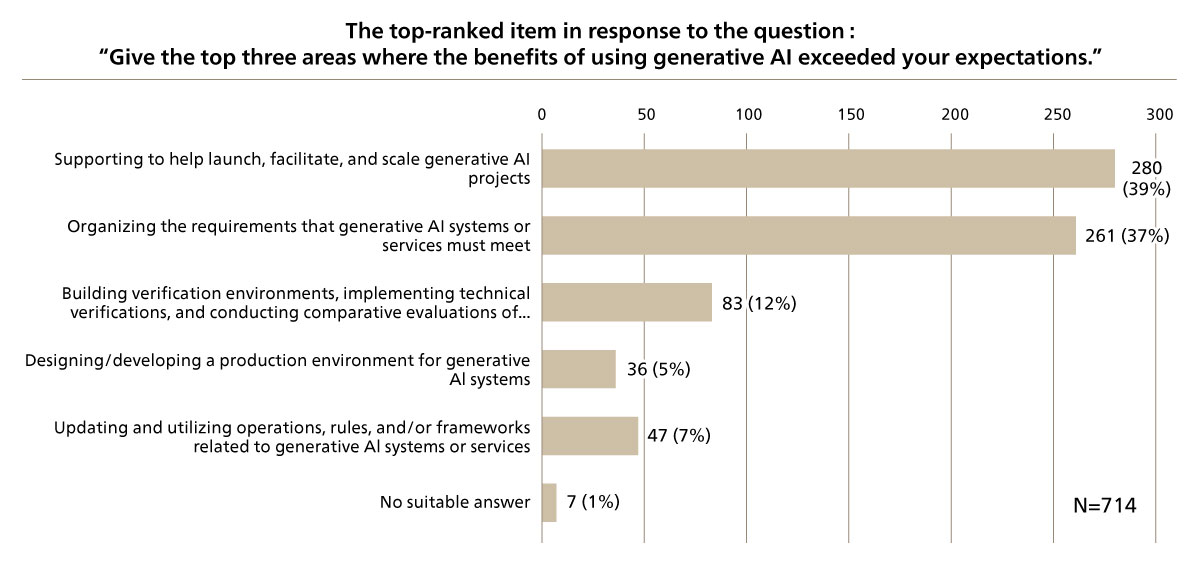 Figure 4 Reasons Why the Effectiveness of Generative AI Exceeded Expectations
Figure 4 Reasons Why the Effectiveness of Generative AI Exceeded Expectations
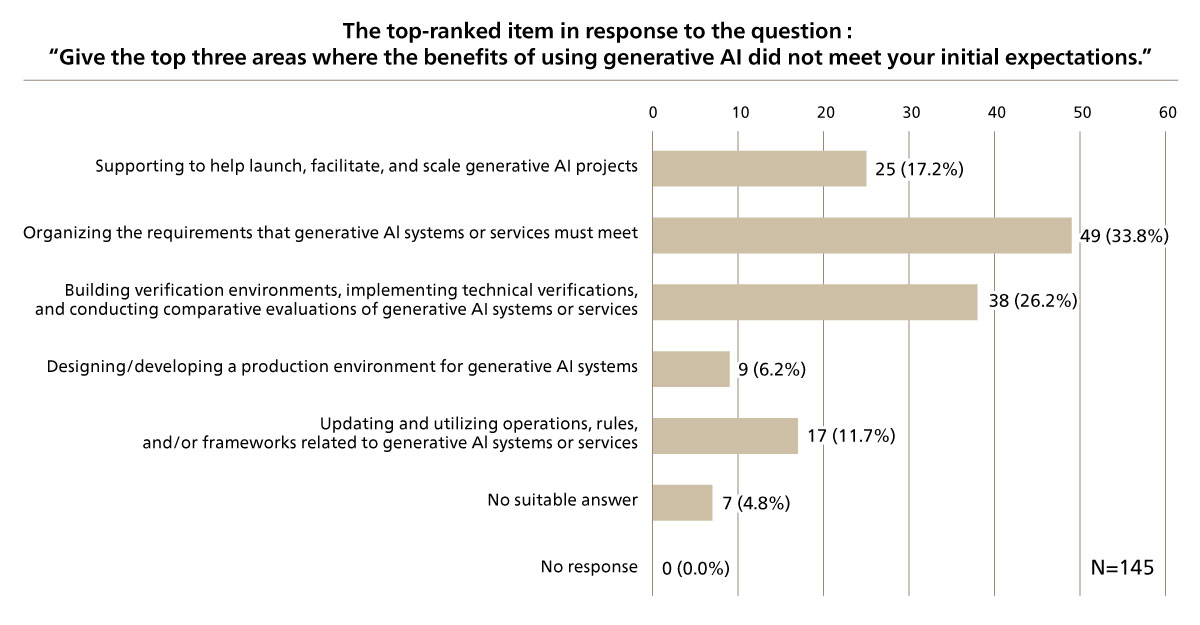 Figure 5 Reasons Why the Effectiveness of Generative AI Fell Short of Initial Expecta
Figure 5 Reasons Why the Effectiveness of Generative AI Fell Short of Initial Expecta
Key points for using generative AI in business operations
How AI is utilized has changed significantly in just two years with the emergence of generative AI. Many companies have begun to adopt generative AI and are starting to reap the benefits. This suggests that simply deploying generative AI and using it for general use cases will not distinguish your company from others or provide a competitive edge over them. It also hints at the importance of further exploring how generative AI can be applied to the specific business challenges and core operations of individual companies.
What do we need to keep in mind to produce a positive impact by using generative AI and to distinguish one’s company from others? At ABeam Consulting, we believe there are four key points to utilizing generative AI:
- To maximize its business value, it is essential to launch company-wide projects and share a vision. The sharing of a strategic vision and adopting an organization-wide approach to deploy generative AI are a must.
- The deployment of generative AI, which presents great ethical and legal risks, requires the designing of a proper business process and an operational management framework. Consideration must be given to how to minimize the risks of generative AI and maximize its business impact.
- The key to operating generative AI effectively is to design a system that can process and accumulate a large amount of unstructured data, version control the models and prompts, and ensure the traceability of output produced from generative AI applications.
- An effective way to deploy generative AI is to adopt an agile approach by conducting a small-scale onsite trial of its use and then repeatedly making improvements. Methods are needed that bridge the gap between onsite expectations and reality to drive the adoption of generative AI in the workplace.
The next Insight will use these key points as a basis for explaining how to specifically advance generative AI utilization.
Insights
- Generative AI-Driven Business Revolution: Seven Keys to Success for Producing Outstanding Results. Part 1: Generative AI-Driven Business Revolution
- Generative AI-Driven Business Revolution: Four Keys to Success for Producing Outstanding Results Part 2: Addressing AI Governance Demanded by Updated Laws and Regulations
- Generative AI-Driven Business Revolution: Four Keys to Success for Producing Outstanding Results Part 3: Our Approach to Getting the Most Out of Company-Wide Usage of Generative AI Beginning with Sharing Your Vision
Click here for inquiries and consultations
